Did you collect respiratory virus infection specimens correctly?
Respiratory viral infections refer to upper respiratory tract infections caused by various viruses, such as colds, laryngitis, bronchitis, etc. For the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory viral infections, accurate specimen collection is very important. Below Mandelab will introduce the collection methods of respiratory virus infection specimens.
Commonly used specimens for respiratory viral infections include nasopharyngeal swabs, cough specimens, and throat swabs. The following is a detailed description of the collection steps for these specimens:
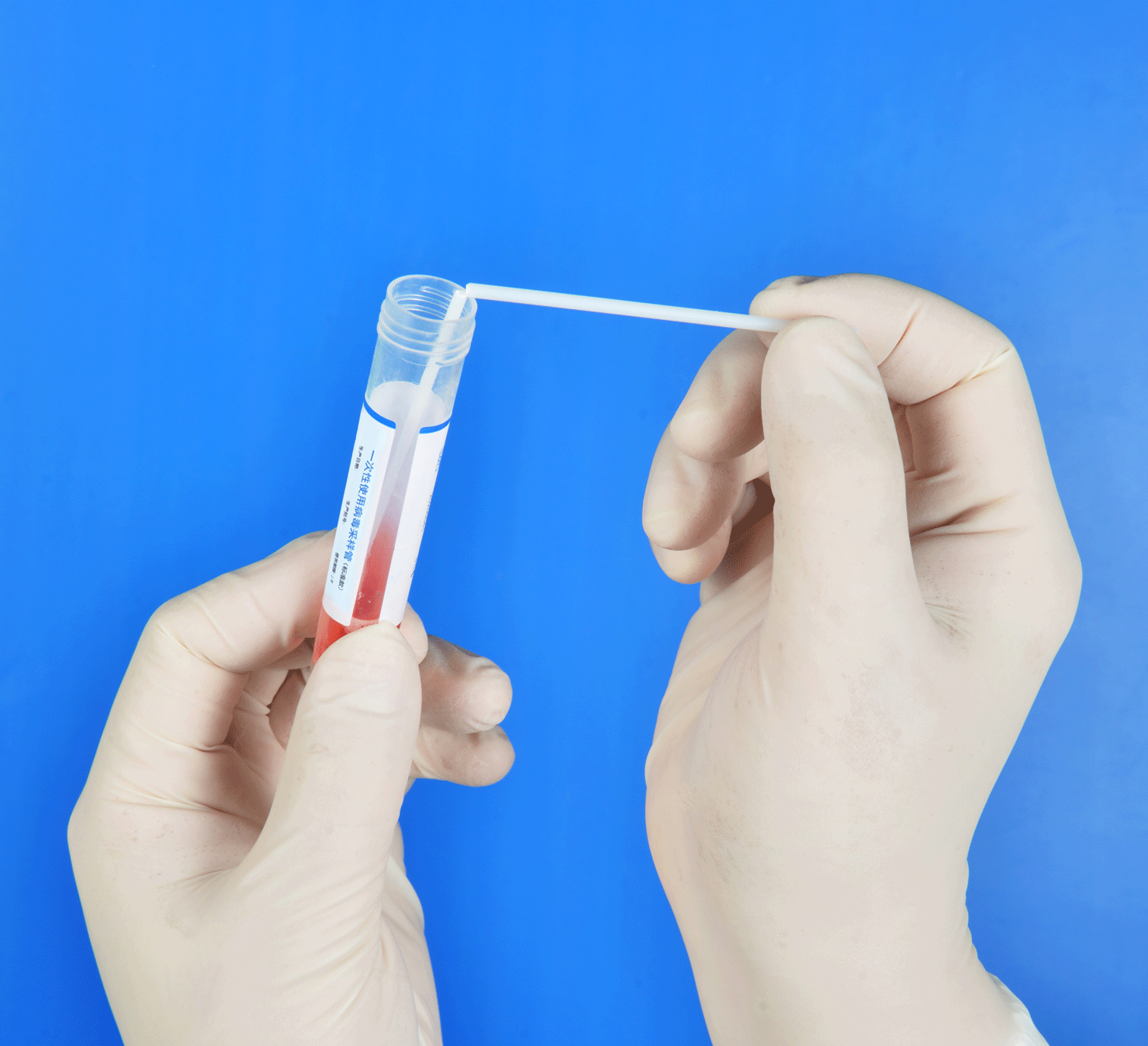
1. Nasopharyngeal swab: This is the most common specimen collection method. First, the sampler needs to wear protective gloves and prepare a disposable sterile nasopharyngeal swab. Next, the person being sampled tilts his or her head back, and the sampler holds the head of the person being sampled with one hand to keep it as stable as possible. The sampler then inserts the sterile nasopharyngeal swab into the patient's nostril and gently rotates it several times to collect an adequate specimen. When finished, place the swab in the preservation solution and close the tube cap tightly.

2. Cough specimen: This specimen is suitable for cases where the person being sampled has cough symptoms. The person being sampled was asked to cough into a sterile container to collect the sputum produced during the cough. The sampler needs to ensure that the sterile container is clean and has sufficient capacity to collect sputum. When finished, close the lid of the container tightly to ensure that the specimen is not contaminated.
3. Throat swab: This is a method of collecting pharyngeal secretions. The sampler first needs to wear protective gloves and prepare disposable sterile throat swabs. Next, the person being sampled should open their mouth and press the tongue with a tongue plate to expose the pharynx. Then, the sampler gently brushes the sterile throat swab across the pharyngeal mucosal surface of the sampled person to ensure that sufficient specimens are collected. After completion, place the throat swab into the preservation solution, break it, and close the tube cap tightly.